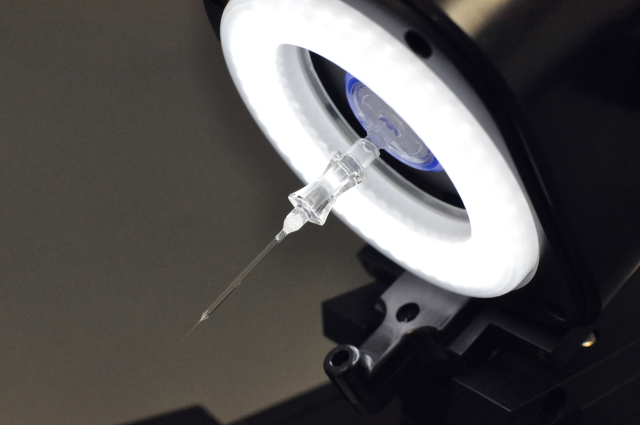
How it works
NDX developed a product line of versatile cell and tissue acquisition instruments (UnipicK™, UnipicK+™ and A-picK™), which are compatible with a wide range of inverted microscopes.
Our technology is based on the improved aspiration principle that utilizes carefully controlled vacuum pulse to acquire desired tissue region or lift attached cells. Instruments range from manually controlled UnipicK™ to fully automated A-picK™ controlled with our proprietary software PIKCELLS™.
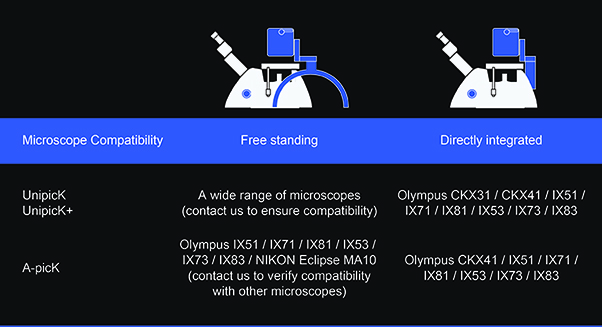
Advantages
Versatility of our instruments ranges from single cell collection to tissue microdissection, including protocols developed for single cell adhesion force measurement and acquisition of regions of interest from fixed tissue specimens such as formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissues.
The instruments can reliably transfer from nanoliter to microliter volumes and fit multiple models of inverted microscopes using our proprietary universal microscope straddle. Both UnipicK+™ and A-picK™ controlling software offer intuitive and self-explanatory program menus to minimize the learning process and facilitate sample acquisition workflow. The systems are compatible with 96-well workflow and may be used for most single cell analysis protocols. In addition, the instruments are highly adaptable to any protocols offering customizable acquisition, dispensing, detachment, and washing parameters.
Notably, all instruments can collect from any standard culture dishes and microscope glass slides using minimal consumables (DCUs), which can be reused if necessary, minimizing overall cost of experimental work. The instruments including fully automated A-picK™ are the most cost-efficient systems on the market, require minimal routine maintenance and come with a standard one year full warranty and up to three years limited warranty.
Summary of advantages
- Cost-efficiency with minimal consumables
- Flexible, fits most inverted microscopes
- High adaptability for customization
- High viability of collected cells
- Versatility in applications
- Functional adhesion test
- Easy to learn and to use
Representative applications
There are numerous applications in the fields of cancer and stem cell research, neuroscience, developmental biology, -omics (e.g. genomics and proteomics) research, pharmaceutical science, lab-on-a-chip technologies, or basic biology. Any research that requires isolation of single cells or acquisition of subanatomical regions can take advantage of our products. Below are some of the common representative applications. Also, please see our sample videos and representative publications.
Single Cell Biology:
- Isolation of single adherent cells from cultures;
- Isolation of rare cells from cultures;
- Isolation of cell clusters or colonies from 3D cultures;
- Clonal expansion of single cells or enrichment;
- Isolation of CTCs from suspensions or placed on a support;
- Isolation of single cells from various biochips;
- Isolation of individual cells from brain sections;
- Measurement of single cell adhesion strength.
Some of the representative publications: Ref1 Ref2 Ref3 Ref4 Ref5 Ref6
Tissue microdissection:
- Microdissection of brain tissues for subanatomical regions and single cell bodies;
- Microdissection of lung, liver, retina, spleen, kidney and other tissues;
- Microdissection of tissue organoids;
- Isolation of regions of interest (ROIs) from fixed tissues including formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissues.
Some of the representative publications: Ref7 Ref8
If you have questions regarding ordering, delivery, installation and training, please see our FAQ